
June 18, 2025
Telecardiology remote monitoring represents one of the most significant advancements in modern cardiovascular care, transforming how healthcare providers diagnose, treat, and manage heart conditions. By leveraging digital technology to transmit cardiac data from patients to healthcare providers in real-time, telecardiology is bridging critical gaps in cardiac care delivery while dramatically improving patient outcomes. This revolutionary approach enables continuous monitoring of heart activity outside traditional clinical settings, allowing for early detection of potentially life-threatening conditions and timely interventions that are literally saving lives every day.
Understanding Telecardiology Remote Monitoring
Telecardiology enables real-time monitoring and analysis of cardiac data from remote locations
Telecardiology remote monitoring integrates telecommunications technology with cardiology to deliver specialized heart care regardless of geographic barriers. This innovative approach allows cardiologists to monitor patients’ cardiac health continuously through various devices that collect and transmit data in real-time, enabling prompt medical interventions when necessary.
At its core, telecardiology encompasses several key components that work together to create a comprehensive remote cardiac care system:
The evolution of telecardiology has been accelerated by advances in digital technology, increased internet connectivity, and the growing need for accessible healthcare solutions. What began as simple telephone transmission of ECG readings has transformed into sophisticated systems capable of monitoring multiple cardiac parameters simultaneously, analyzing data through artificial intelligence, and facilitating immediate clinical decisions.
How Telecardiology Remote Monitoring Works
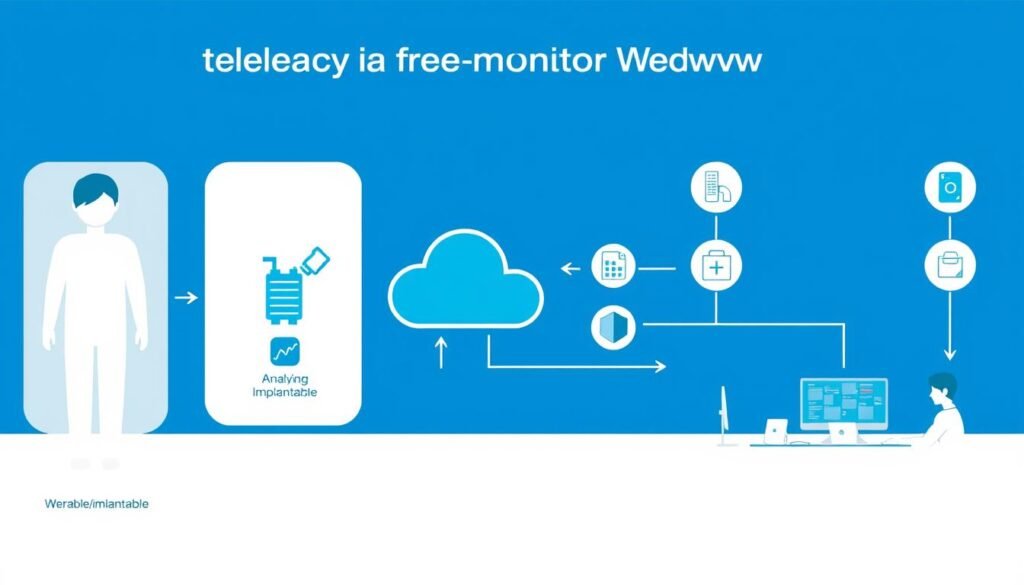
The telecardiology ecosystem: From patient devices to clinical intervention
Monitoring Devices and Data Collection
The foundation of telecardiology remote monitoring lies in the devices that capture cardiac data. These range from external wearables to sophisticated implantable devices:
Data Transmission and Security
Once collected, cardiac data must be securely transmitted to healthcare providers for analysis:
Analysis and Clinical Response
The final component involves healthcare professionals interpreting the data and taking appropriate action:
Want to understand how telecardiology systems work in detail?
Download our comprehensive infographic explaining the complete telecardiology monitoring workflow from patient devices to clinical intervention.
Download InfographicLives Saved Through Telecardiology Remote Monitoring

Telecardiology enables timely interventions through continuous monitoring and virtual consultations
The impact of telecardiology remote monitoring extends beyond theoretical benefits—it’s saving lives daily through early detection and intervention. Here are five documented cases where telecardiology made the critical difference:
Case 1: Early Detection of Silent Heart Attack
A 67-year-old man with a history of coronary artery disease was using an implantable cardiac monitor as part of his post-stent telecardiology program. The device detected subtle ST-segment changes that didn’t trigger symptoms but indicated a potential silent myocardial infarction. His cardiologist received an alert, contacted the patient immediately, and directed him to the emergency room. Angiography revealed a 95% blockage in a previously stented artery. Prompt intervention with another stent prevented a major heart attack that likely would have gone undetected until causing significant damage or death.
Case 2: Preventing Stroke Through Atrial Fibrillation Detection
A 72-year-old woman with no previous cardiac history was using a smartwatch with ECG capabilities. The device detected an irregular rhythm and prompted her to record an ECG, which suggested atrial fibrillation. She shared the data with her physician through the telecardiology platform, leading to immediate anticoagulation therapy. Two weeks later, a formal diagnosis confirmed persistent atrial fibrillation. According to her cardiologist, the early detection and treatment likely prevented a stroke, as untreated atrial fibrillation significantly increases stroke risk.
Case 3: Remote Heart Failure Management
A 58-year-old man with chronic heart failure was enrolled in a comprehensive telecardiology program that monitored his weight, blood pressure, heart rate, and symptoms daily. The system detected a 4-pound weight gain over three days, decreased heart rate variability, and increased nighttime heart rate—all subtle signs of heart failure decompensation. His medication was adjusted remotely before symptoms became severe. This intervention prevented what would have been his fourth hospitalization that year, avoiding the 30% mortality risk associated with each heart failure hospitalization.
“Telecardiology isn’t just improving convenience—it’s fundamentally changing outcomes. We’re catching life-threatening conditions days or even weeks before they would have been detected in traditional care models.”
Dr. Jennifer Mathers, Director of Digital Cardiology, University Medical Center
Case 4: Life-Saving ICD Intervention
A 45-year-old man with an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) for primary prevention of sudden cardiac death was at home when his device detected ventricular tachycardia. The ICD delivered appropriate therapy and immediately transmitted the event data to his cardiologist through the telecardiology system. The physician noted that this was the patient’s first arrhythmic event and scheduled an immediate virtual consultation, followed by medication adjustments. Remote monitoring continued to track the effectiveness of the new treatment regimen, preventing further dangerous arrhythmias.
Case 5: Medication-Induced QT Prolongation
A 63-year-old woman started a new antibiotic known to potentially prolong the QT interval. As part of her care plan, she was equipped with a mobile ECG monitor that transmitted daily readings to her cardiologist. On the third day of treatment, the system detected significant QT prolongation, a condition that can lead to life-threatening arrhythmias. Her medication was immediately discontinued, and alternative treatment was prescribed. Without telecardiology monitoring, this dangerous side effect might have gone undetected until causing a potentially fatal arrhythmia.
Benefits of Telecardiology Remote Monitoring

Telecardiology bridges the gap between patients in remote areas and specialized cardiac care
Early Detection and Intervention
One of the most significant advantages of telecardiology remote monitoring is the ability to detect cardiac issues before they become life-threatening:
Reduced Hospitalizations and Healthcare Costs
Telecardiology has demonstrated significant impact on reducing the need for emergency care and hospitalizations:
Improved Access to Specialized Cardiac Care
Telecardiology bridges significant gaps in access to specialized cardiac care:
Enhanced Patient Engagement and Satisfaction
Telecardiology promotes greater involvement of patients in their cardiac care:
| Outcome Measure | Traditional Cardiac Care | Telecardiology Remote Monitoring | Improvement |
| Time to detection of arrhythmias | 42 days (average) | 5.5 days (average) | 87% faster |
| Heart failure hospitalizations | 1.4 per patient-year | 0.7 per patient-year | 50% reduction |
| Emergency department visits | 2.8 per patient-year | 0.9 per patient-year | 68% reduction |
| Medication adherence | 63% adherence rate | 89% adherence rate | 41% improvement |
| Patient satisfaction | 72% satisfaction score | 91% satisfaction score | 26% improvement |
| Annual healthcare costs | $26,700 per patient | $18,300 per patient | 31% savings |
Challenges and Considerations in Telecardiology Implementation

Technology adoption remains a challenge, particularly among elderly patients
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
As with all digital health technologies, telecardiology remote monitoring systems must address significant privacy and security challenges:
According to a Department of Health and Human Services report, healthcare organizations implementing telecardiology must develop comprehensive security frameworks that address these concerns while maintaining system usability.
Technology Literacy and Access Barriers
The effectiveness of telecardiology depends on patients’ ability to use the required technology:
Integration with Existing Healthcare Systems
Implementing telecardiology within established healthcare frameworks presents significant challenges:
Clinical and Technical Limitations
Despite its benefits, telecardiology has inherent limitations that must be acknowledged:
Advantages of Telecardiology Remote Monitoring
- Early detection of cardiac events
- Reduced hospitalizations and emergency visits
- Improved access to specialized care
- Enhanced patient engagement
- Cost savings for healthcare systems
- Continuous monitoring capability
- Reduced travel burden for patients
Challenges of Telecardiology Remote Monitoring
- Data privacy and security concerns
- Technology literacy barriers
- Infrastructure requirements
- Integration with existing systems
- Reimbursement complexities
- Potential for false alarms
- Limited physical examination capability
Telecardiology Adoption: Current Statistics and Trends
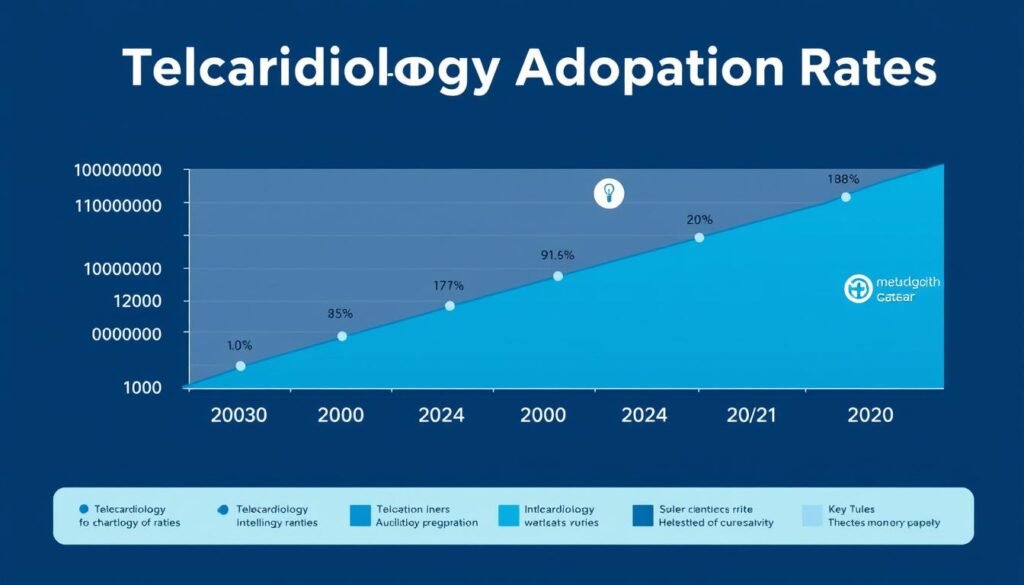
Telecardiology adoption has accelerated significantly since 2020, with continued growth projected through 2024
The adoption of telecardiology remote monitoring has accelerated dramatically in recent years, driven by technological advancements, changing reimbursement policies, and the COVID-19 pandemic’s impact on healthcare delivery models.
Global Telecardiology Market Growth
Recent market analyses reveal substantial growth in the telecardiology sector:
Clinical Implementation Statistics
Healthcare systems are increasingly integrating telecardiology into standard cardiac care:
Patient Adoption Trends
Patient acceptance and utilization of telecardiology services continue to grow:
Reimbursement and Policy Developments
Evolving healthcare policies are increasingly supporting telecardiology implementation:
Case Study: Successful Telecardiology Implementation

Midwest Regional Health System’s telecardiology command center monitors patients across five states
Midwest Regional Health System’s Telecardiology Program
Midwest Regional Health System (MRHS) implemented a comprehensive telecardiology remote monitoring program in 2021 that has become a model for healthcare systems nationwide. Serving a five-state region with significant rural populations, MRHS faced challenges including cardiologist shortages, long travel distances for patients, and high rates of cardiovascular disease.
Implementation Strategy
MRHS developed a phased approach to telecardiology implementation:
Technical Infrastructure
The MRHS telecardiology program utilizes a multi-layered technical approach:
Results and Outcomes
After two years of full implementation, MRHS has documented significant improvements in cardiac care:
Key Success Factors
MRHS identified several critical elements that contributed to their successful implementation:
“Our telecardiology program has fundamentally transformed how we deliver cardiac care. We’re reaching patients we never could before, intervening earlier, and achieving outcomes that weren’t possible with traditional models. The investment has paid for itself many times over in both financial terms and, more importantly, in lives saved.”
Dr. Michael Renner, Chief of Cardiology, Midwest Regional Health System
Learn from MRHS’s successful implementation
Download our detailed case study with implementation timeline, technical specifications, and ROI analysis of the Midwest Regional Health System telecardiology program.
Get the Complete Case StudyThe Future of Telecardiology Remote Monitoring
Next-generation telecardiology systems will leverage AI for predictive analytics and personalized care
Artificial Intelligence Integration
The integration of artificial intelligence is poised to revolutionize telecardiology remote monitoring:
Advanced Wearable and Implantable Technologies
Next-generation monitoring devices will offer expanded capabilities and improved patient experience:
Predictive Analytics and Personalized Care
The future of telecardiology will increasingly focus on predictive and personalized approaches:
Expanded Applications and Integration
Telecardiology is expanding beyond traditional applications to address broader aspects of cardiovascular health:

Next-generation wearable devices will offer improved comfort and expanded monitoring capabilities
Conclusion: The Transformative Impact of Telecardiology
Telecardiology remote monitoring represents a paradigm shift in cardiovascular care delivery, fundamentally changing how cardiac conditions are detected, monitored, and managed. By enabling continuous surveillance of cardiac parameters outside traditional clinical settings, telecardiology is facilitating earlier interventions, improving access to specialized care, reducing hospitalizations, and ultimately saving lives.
The documented benefits of telecardiology—from 50% reductions in heart failure hospitalizations to dramatic improvements in patient satisfaction and medication adherence—demonstrate its value for patients, providers, and healthcare systems alike. While challenges related to technology access, data security, and system integration remain, ongoing advancements and policy developments continue to address these barriers.
As telecardiology evolves with artificial intelligence, advanced wearables, and predictive analytics, its capabilities will expand further, enabling increasingly personalized and proactive cardiac care. For healthcare organizations, implementing telecardiology is no longer simply an option but an essential strategy for delivering high-quality, accessible, and cost-effective cardiovascular care in the modern era.
The future of cardiology is increasingly remote, connected, and intelligent—and the beneficiaries are patients who receive better care and the healthcare systems that can deliver it more efficiently than ever before.
Ready to implement telecardiology remote monitoring?
Download our comprehensive implementation guide with step-by-step instructions, technology requirements, and best practices for establishing an effective telecardiology program.
Download Implementation Guide





